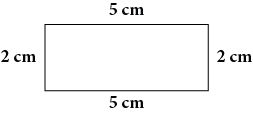Introduction: Connecting Your Learning
 This module discusses perimeter and circumference of geometric figures. By the end of this lesson, you should be familiar with the definition of polygon, diameter and radius of a circle, and how to calculate the perimeter and circumference of a circle.
This module discusses perimeter and circumference of geometric figures. By the end of this lesson, you should be familiar with the definition of polygon, diameter and radius of a circle, and how to calculate the perimeter and circumference of a circle.
Be careful not to overlook the beginning of this lesson. The lesson opens with the definition of a polygon. Sometimes polygons are oddly shaped; they are not usually your typical rectangles and squares. Within modern architecture, there is a good possibility that you may work in office spaces that are oddly shaped in design. You might be asked to work in or set up work spaces in offices that have no right angles or possibly no straight walls.
As you work through this lesson, visualize how you would lay out your office or a grouping of work stations within these oddly shaped rooms in order to reduce the amount of network cabling you will need to purchase.
Focusing Your Learning
Lesson Objectives
By the end of this lesson, you should be able to:
- Define polygon.
- Calculate the perimeter of common geometric shapes.
- Calculate the circumference, the diameter, and the radius of a circle.
Presentation
Polygon
What is a polygon?
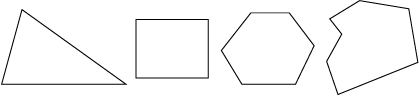
A polygon is a closed plane (flat) figure whose sides are line segments (portions of straight lines).
Polygons
Not Polygons
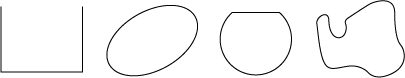
 |
Select the following link to visit a Web site that provides a detailed explanation of what a polygon is. The site also provides examples to help you better understand this newly introduced geometric shape. |
Perimeter
What does the term perimeter mean?
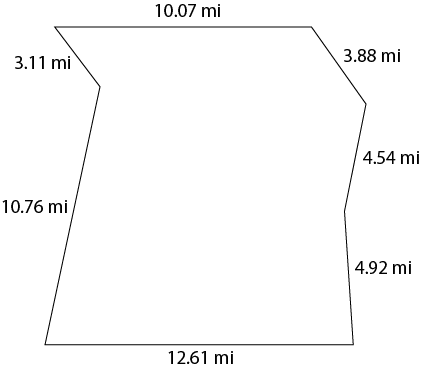
The perimeter of a polygon is the distance around the polygon.
To find the perimeter of a polygon, you add up the lengths of all the sides.
Take a look at the following examples to see how to find the perimeter of each polygon.
Perimeter = 2 cm+5 cm+2 cm+5 cm = 14 cm |
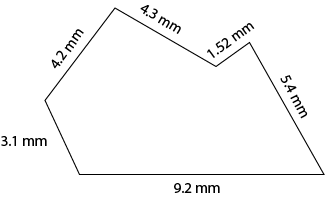
Perimeter = 3.1 mm +4.2 mm +4.3 mm +1.52 mm+ 5.4 mm +9.2 mm = 27.72 mm |
Here is one more example that shows how to determine the area when a measurement is missing.
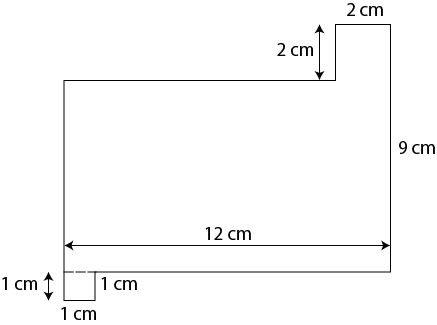
You will notice that three of the dimensions are missing. However, you can determine the missing measurements using the following process. Let A, B, and C represent the missing measurements.

A = 12 m – 2 m = 10 m
B = 9 m + 1 m – 2 m = 8 m
C = 12 m – 1 m = 11 m
Perimeter = 8 m + 10 m + 2 m + 2 m+ 9 m + 11 m + 1 m +1 m = 44 m
 |
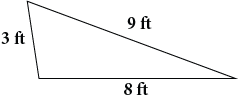
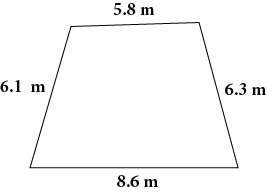
Now that you have reviewed the examples, it is time to practice on your own. Find the perimeter of each polygon below then select Check Your Answers to see how well you did. You will need a sheet of paper and a pencil to complete this practice activity. |
Circumference, Diameter, and Radius
What is the circumference of a circle?
The circumference of a circle is the distance around the circle.
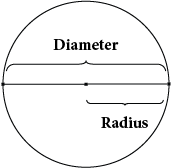
Diameter
What is the diameter of a circle?
The diameter of a circle is any line segment that passes through the center of the circle and has its endpoints on the circle.
Radius
What is the radius of a circle?
The radius of a circle is any line segment having as its endpoints the center of the circle and a point on the circle. The radius equals one-half the diameter.
The Number π
What does the symbol π mean?
The symbol π, read "pi," represents the nonterminating, nonrepeating decimal number 3.14159...
For computational purposes, π is often approximated as 3.14. You write π ≈ 3.14 to denote that π is approximately equal to 3.14. The symbol "≈" means "approximately equal to."
Now that you have a better understanding of the terms circumference, diameter, radius, and pi- π ≈ 3.14, it is time to learn the formula you will need to compute the circumference of a circle.
- To find the circumference of a circle, you only need to know its diameter or radius. You then use a formula for computing the circumference of the circle.
- If C, d, and r represent the circumference, diameter, and radius, respectively, of a circle, the following two formulas give directions for computing the circumference of the circle.
Circumference Formulas
C = πd or C ≈ (3.14) d
C = 2πr or C ≈ 2 (3.14) r
Take a look at the following examples to see how to determine the circumference of a circle.
Example 1
Find the exact circumference of the circle.

Use the formula C = πd.
C = π ⋅ 7 in.
By the commutative property of multiplication,
C = 7 in. ⋅ π
C =7π in., exactly
This result is exact since π has not been approximated.
Example 2
Find the approximate circumference of the circle.
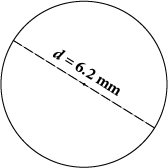
Use the formula C = πd.
C ≈ (3.14)(6.2)
C ≈ 19.648 mm
This result is approximate since π has been approximated by 3.14.
Example 3
Find the approximate circumference of a circle with radius of 18 in.
Since you know that the radius r is 18 in., use the formula C = 2πr.
C ≈ (2)(3.14)(18 in.)
C≈113.04 in.
For additional explanations and working examples of how to find the perimeter of a polygon and the circumference of a circle watch the following Khan Academy videos.
 |
Math Video Toolkit |
Practice: Perimeter and Circumference
 |
Now you have the chance to work out some problems. You may use a calculator if you would like. Study each of these problems carefully; you will see similar problems on the lesson knowledge check. Select the following link to complete the practice activity. You will need to get out a piece of paper and a pencil to complete the practice problems. Finding the Perimeter and Circumference Practice Problems Once you complete the practice activity, check to see how well you did by selecting the following link: |
Summarizing Your Learning
In this lesson, you learned about polygons and how to measure their perimeters. For most of the shapes, you add up the lengths of all the sides. For circles, you use the formula C = 2πr or C = πd.
Assessing Your Learning
 |
Now that you have read over the lesson carefully and attempted the practice problems, it is time to test your knowledge. Please note that this is a graded part of this lesson so be sure you have prepared yourself before starting. |
- Complete the Geometric Figures: Perimeter and Circumference.
Resource:
“Measurement and Geometry: Area and Volume of Geometric Figures and Objects” by Ellis, W., & Burzynski, D. © 2010 retrieved from http://cnx.org/content/m35023/1.2/ is used under a Creative Commons Attribution http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/. This is an adaption of the lesson titled, “Perimeters and Circumference,” by the National Information Security and Geospatial Technologies Consortium (NISGTC) is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0